Below is the online edition of In the Beginning: Compelling Evidence for Creation and the Flood,
by Dr. Walt Brown. Copyright © Center for Scientific Creation. All rights reserved.
Click here to order the hardbound 8th edition (2008) and other materials.
51. Mountains of Venus
Venus must have a strong crust to support its high, densea mountains. One mountain, Maat Mons, rises higher than Earth’s Mount Everest does above sea level. Because Venus is relatively near the Sun, its atmosphere is 860°F—so hot its surface rocks must be weak or “tarlike.” (Lead melts at 622°F and zinc at 787°F.) Only if Venus’ subsurface rocks are cold and strong can its mountains defy gravity. This allows us to draw two conclusions, both of which contradict major evolutionary assumptions.
First, evolutionists assume that planets grew (evolved) by rocky debris falling in from outer space, a process called gravitational accretion. Heat generated by a planet’s worth of impacts would have left the rocky planets molten. However, Venus was never molten. Had it been, its hot atmosphere—a runaway greenhouse composed of supercritical carbon dioxide—would have prevented its subsurface rocks from cooling enough to support its mountains. So, Venus did not evolve by gravitational accretion.
Secondly, evolutionists believe that the entire solar system is billions of years old. If Venus were billions of years old, its atmospheric heat would have “soaked” deeply enough into the planet to weaken its subsurface rocks. If so, not only could Venus’ crust not support mountains, the hot mountains themselves could not maintain their steep slopes. Venus must be relatively young.
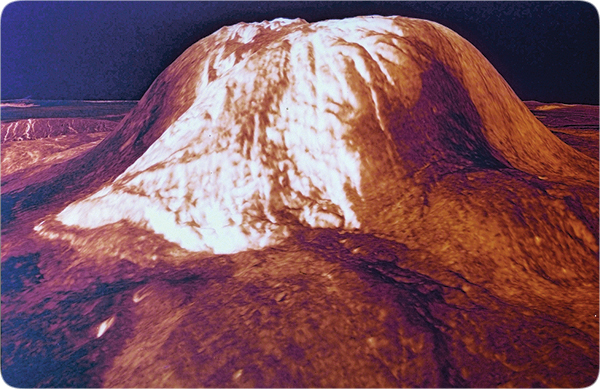
Figure 26: Maat Mons on Venus. If Venus’ mountains were composed of lighter material, they would “float” in the denser rock below, similar to an iceberg floating in denser liquid water. (Mountains on Earth are buoyed up, because they have a density of about 2.7 gm/cm3 and “float” in rock that is about 3.3 gm/cm3.) Data from the Magellan spacecraft that orbited and mapped Venus for several years showed that Venus’ mountains are composed of rock that is too dense to “float.” So, what supports them? It must be Venus’ strong crust—despite Venus’ extremely hot atmosphere. This implies Venus is not old and did not evolve.